说在前面
最近,Java写恶心了,计划重新捡起丢在一边很久的Scala,但是,Scala是个大怪物,几年前刚接触Scala的时候,认认真真地读过一遍原版《Programming in Scala : A Comprehensive Step-by-step Guide》,但是完全迷失在一堆难于理解的概念中。回头细想,本质上还是缺乏函数式编程的功底。为了更好地理解函数式编程的核心理念,我就用Haskell这门纯粹的函数式语言作为起点,开启我的重拾Scala之路。
Install Haskell Environment in Mac Step By Step
1 | % brew install ghc cabal-install |
1 | % ghci |
Basic Concepts
定义函数
1 | Prelude> let double x = x * 2 |
定义模块
1 | ./double.hs |
1 | Prelude> :load double.hs |
递归
递归的不同实现 -> 阶乘问题
一行递归
1 | Prelude> let fact x = if x==0 then 1 else fact (x - 1) * x |
模式匹配
1 | ./factorial.hs |
哨兵表达式
1 | ./fact_with_guard.hs |
高效地处理递归,元祖和列表 -> Example: 斐波那契序列问题
不够高效的实现:模式匹配
1 | ./fib.hs |
高效实现:利用元组,转换为尾递归
1 | ./fib_tuple.hs |
利用函数的组合
1 | ./fib_pair.hs |
高阶函数
匿名函数(lambda)
1 | Prelude> (\x -> x ++ "World!") "Hello " |
map
1 | -- map + lamda |
filter
1 | *Main> filter odd [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] |
flodl, foldr
1 | Prelude> foldl (\x carryOver -> carryOver + x) 0 [1 .. 10] — fold from left to right |
foldl的一种简化表达: fold1
1 | Prelude> foldl1 (+) [1 .. 10] |
Advanced Concepts
偏应用函数:将多参数的函数拆分为多个只有一个参数的函数
1 | -- 发现偏应用 |
1 | -- 偏应用:绑定函数的一部分参数 |
偏应用函数的运算过程称为柯里化
- prod 2 4 实际上计算(prod 2) 4
- 几乎每个Haskell的多参数函数都是柯里化的
惰性求值: 仅仅完成一部分必要的计算
1 | -- 可以构造无穷列表 |
类型系统
原生类型
1 | Prelude> :set +t |
自定义类型(利用data关键字定义)
1 | ./cards-with-show.hs |
注:deriving用于函数的继承,代码段中继承了show函数用于在控制台中显示自定义数据类型Suit和Rank
1 | Prelude> :load cards-with-show.hs |
类型模板 -> 实现函数的多态以及数据类型的多态
1 | ./type_template.hs |
自定义类型模板
1 | ./userdefine_type_template.hs |
1 | *Main> :load userdefine_type_template.hs |
注:Triplet: 类型构造器,Trio: 数据构造器
自定义递归类型
1 | ./tree_depth.hs |
1 | *Main> :load tree_depth.hs |
类
- 为了便于实现函数的继承、重载、多态
- 不同于面向对象中的Class:对象是类型,不涉及数据
1 | -- 内置的Eq类,实现了相等判断 |
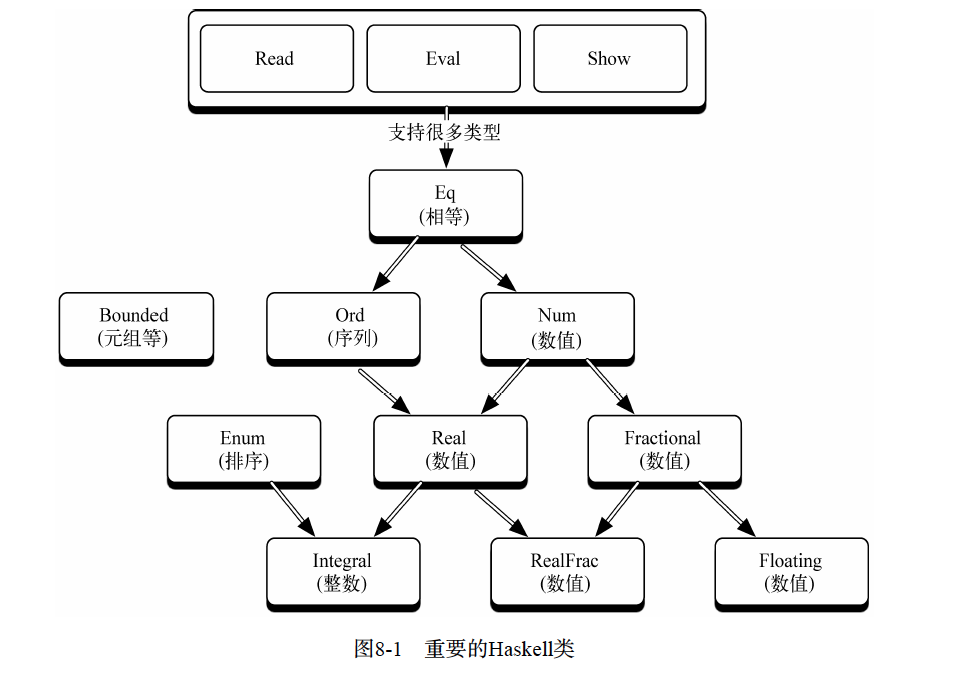
Monad
- 本质上,一个Monad是一个函数组合
- 以特定属性的方式组合函数替代原来的嵌套调用,
- 一个monad = 类型容器 + return函数 + >>==bind函数
用途:
- 可以用于模拟程序的状态,从而实现用纯函数式较难实现的事情,比如IO
- 基于moand实现的do语法可以支持命令式风格的编程
- Maybe monad可以用来进行错误处理
Example 1:醉汉问题
嵌套方式实现
1 | ./drunken-pirate-without-monad.hs |
利用Monad实现
1 | ./drunken-pirate-monad.hs |
1 | *Main> treasureMap (Position 0) |
Example 2: 利用do实现I/O monad
1 | ./io-monad.hs |
1 | Prelude> :load io-monad.hs |
Reference

订阅我的微信公众号,您将即时收到新博客提醒!